Objective To explore the method of treatment for cirrhosis associated portal hypertension and hepatogenic diabetes.
摘要目的探讨肝硬化门静脉
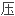
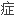 合并肝源
合并肝源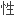 糖尿病的
糖尿病的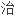
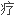
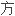 法。
法。
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。
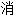 化
化 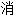 化
化  化
化  化
化  化
化  化
化  化
化  化
化  化
化  化
化 The gold standard for determining if there is portal hypertension is obtaining a hepatic venous pressure gradient measurement where a catheter is inserted inside the inferior vena cava and then inside the portal vein to measure the difference between both pressures.
确定是否存在门静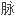

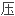
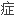 的金标准是测量肝静
的金标准是测量肝静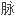
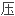 力梯度,即将导管先后插入下腔静
力梯度,即将导管先后插入下腔静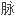 、门静
、门静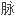 内测量两个
内测量两个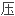 力之间的差异。
力之间的差异。